What Best Describes the Resting Membrane Potential
The membrane potential can change for example when the neurone is actively engaged in information transmission via generation of action potentials. A The Nernst equation can predict whether an ion is in electrochemical.
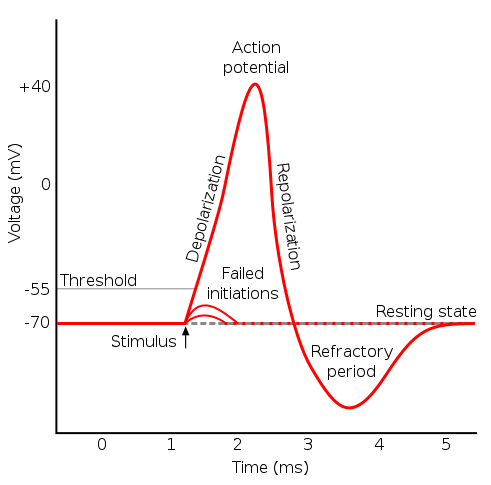
Action Potential The Resting Membrane Potential Generation Of Action Potentials Teachmephysiology
It is caused by differences in the concentrations of ions inside and outside the cell.
. What has been described here is the action potential which is presented as a graph of voltage over time in Figure 1257. A The Nernst equation can predict whether an ion is in electrochemical equilibrium. The membrane potential of the electrically inactive neurones is known as the resting membrane potential.
See the answer See the answer done loading. Resting Potential A cell membrane separates one charge on the cells interior from another charge on the cells exterior. Which of the following statements best describes the neural membrane during the resting phase.
Which of the following describes the resting membrane potential of a neuron. The resting membrane potential of a nerve cell is -70 mV which indicates that the intracellular region of the nerve cell has a negatively charged environment in. The above equation Eq.
Which of the following best describes the resting membrane potential RMP. The action of these pumps combined with the diffusion of certain ions through protein channels in the membrane results in a resting membrane potential of approximately 70mV with. The resting potential is determined by concentration gradients of ions across the membrane and by membrane permeability to each type of ion.
The resting membrane potential is restored by the closing of sodium activation gates and the opening of the voltage-gated K channel which stops the flow of Na and allows the outward. Which of these statements best describes the Nernst equation and the resting membrane potential. A resting non-signaling neuron has a voltage across its membrane called the resting membrane potential or simply the resting potential.
This voltage is called the resting membrane potential. If the membrane were equally permeable to all ions each type of ion would flow across the membrane and the system would reach equilibrium. It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for.
The resting membrane potential of a cell is defined as the electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane when the cell is in a non-excited state. Define resting membrane potential and describe its electrochemical basis. The potential difference in a resting neuron is called the resting membrane potential.
The value of the resting membrane. A voltage difference across the. When a cell is resting the fluid inside of it is a little bit.
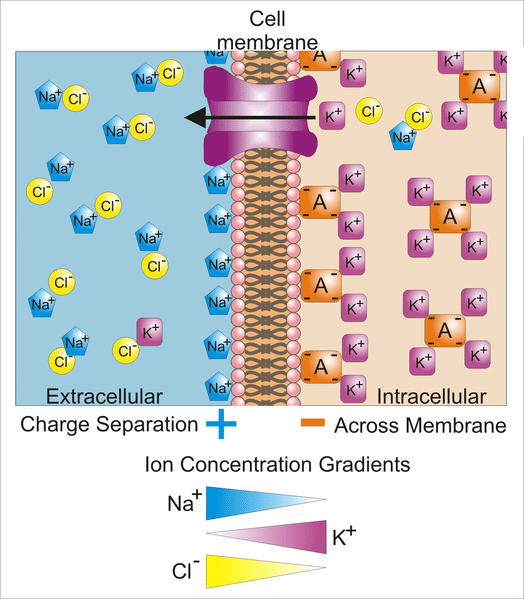
5 is known as the Nernst equationThe Nernst equation allows us to calculate the potential that will be established across the membrane based on the. The plasma membranes of resting axons are slightly polarized due to the unequal distribution of Na K Cl- and protein- ions in ECF and ICF. A typical neurons resting membrane potential is approximately -65 mV.
Top Answer A Explanation. Several factors play a role in. All of the voltage gated sodium and potassium channels are closed.
The intracellular environment is negatively charged A clinician induces contraction of the gastrocnemius and. The inside of a cell is approximately 70 millivolts or - 70 mV This typical value of resting membrane potential is called the resting membrane potential more negative than the outside. Briefly discuss changes to resting membrane potential.
Which of these statements best describes the Nernst equation and the resting membrane potential. Which of the following statements best describes the resting membrane potential. This causes the membrane to be polarized.
A a concentration gradient that exists between the intracellular and extracellular fluids B the. It is negative because resting membrane is permeable mainly to K and there is a concentration gradient. A voltage difference of 0 millivolts mV across the membrane.
Resting membrane potential is the electrical potential energy voltage that results from separating opposite charges across the plasma membrane when those charges are not.
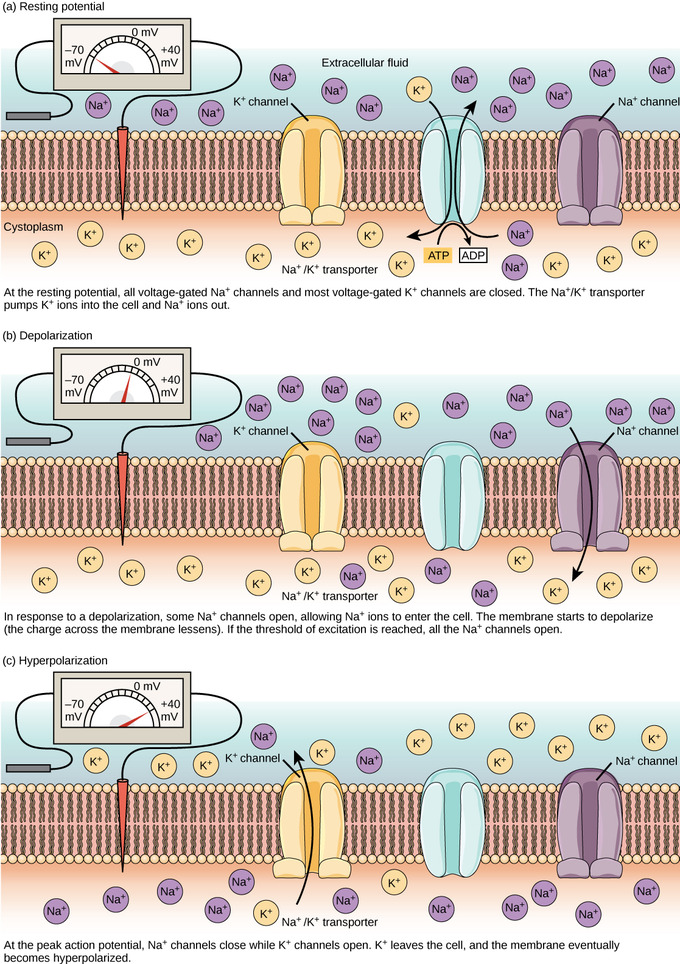
How Neurons Communicate Boundless Biology
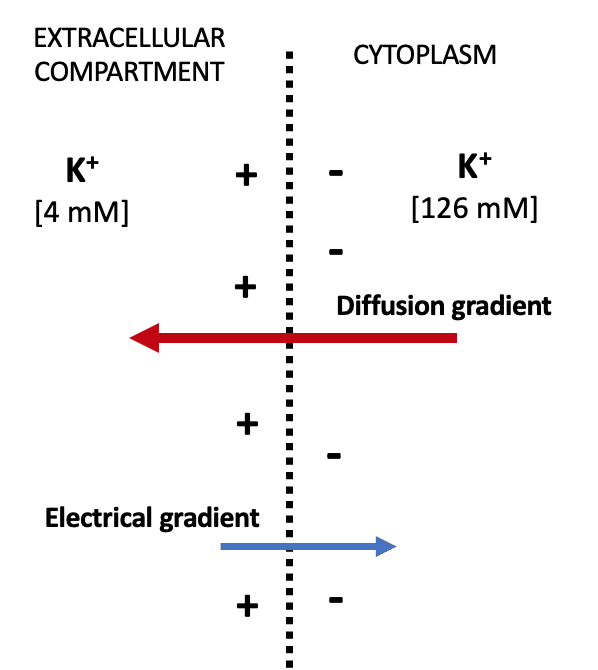
Resting Membrane Potential Nernst Generation Teachmephysiology

Action Potential The Resting Membrane Potential Generation Of Action Potentials Teachmephysiology

No comments for "What Best Describes the Resting Membrane Potential"
Post a Comment